what does it mean to be elected at large
At-large is a description for members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent a whole membership or population (notably a city, county, state, province, nation, club or association), rather than a subset. In multi-hierarchical bodies the term rarely extends to a tier beneath the highest division. A contrast is implied, with certain balloter districts or narrower divisions. Information technology tin can be given to the associated territory, if any, to denote its undivided nature, in a specific context. Unambiguous synonymous are the prefixes of cross-, all- or whole-, such as cross-membership, or all-state.
The term is used equally a suffix referring to specific members (such as the U.S. congressional Representative/the Member/Rep. for Wyoming at large). It figures equally a generic prefix of its subject thing (such as Wyoming is an at-large U.Southward. congressional district, at present). It is unremarkably used when making or highlighting a direct contrast with subdivided equivalents that may be by or nowadays, or seen in exotic comparators. If fairly practical it indicates that the described zone has no further subsets used for the aforementioned representative purpose. A off-white exception is a cipher-exceptions arrangement of overlapping tiers (resembling or being district and regional representatives, ane set of which is at large) for render to the very same chamber, and consistent issue of multiple ballots for plural voting to every voter. This avoids plural voting competing with single voting in the jurisdiction, an inherent unlike level of autonomous power.
Examples of a autonomous power disparity were establish in a small number of states at certain U.Due south. Congresses, between 1853 and 1967, and in the old lower houses of Uk and Ireland, whereby certain voters could vote for (and entrance hall) at-big (whole-country/Canton) and commune(-based) representatives to them, giving zones of plural voting and thus representation contrasting with zones, for the aforementioned national assembly, of single voting and representation.[1] [2] In 1964 the U.S. Supreme Court banned such plural voting for the Usa Congress (thus banning at-large, whole-state congressional districts which overlap state subdivision congressional districts).
Universal principles utilise regardless whether election(s) are for an at-big member, or not.
- a single seat/position/representative: entails a unmarried-winner voting system;
- a console/slate/group of seats/positions/representatives: involves some other arrangement. It is usually proportional representation (whether in "pure" party-list form, as a party-list proportional tier of a mixed-member or parallel voting arrangement, or STV leading forms), Single not-transferable vote (basic single-choice, multi-member), or cake (basic multi-option, multi-member) voting.
Canada [edit]
Some municipalities in Canada elect role or all of their city councils at-large. The class of municipal election is widespread in small towns to avoid "them and us" cultural dissociation of dividing them into wards. Notable larger instances are, from west to east:
- The chief cities of British Columbia: Vancouver, Victoria, Surrey and Richmond (all councillors, at-large. They adopt specialist spokesman, executive or commission roles).
- St. Albert, Alberta and almost all other municipalities in Alberta (excepting Wood Buffalo and Edmonton) (all councillors at-big)
- Portage la Prairie, Manitoba (all councillors at-large)
- N Bay, Ontario (all councillors at-big)
- Thunder Bay, Ontario (seven councillors elected to wards, five councillors elected at-large)
- Timmins, Ontario (4 rural wards with one councillor each, one urban ward with four at-large councillors)
The 3 territories: Yukon, Nunavut and the Northwest Territories are federally served in the Parliament of Canada by one at-big Member of Parliament and Senator each. These take high apportionment only are ethnically diverse and of exceptional size. Provinces are divided to make upwards the other 335 electoral districts (ridings or comtés). The latter are combined into large regions to select the other 102 senators.
State of israel [edit]
In Israel, elections for the Knesset (the national parliament) are conducted on an at-large basis past proportional representation from party lists. Ballot of municipal and town (but not regional) councils are on the aforementioned basis.
Netherlands [edit]
In holland, elections for the Business firm of Representatives (the lower business firm of the states-Full general, the national parliament) are conducted on an at-large footing by proportional representation from party lists.
Philippines [edit]
This style of election applies to the Senate. All voters tin bandage twelve votes to refresh half of the senate, namely twelve senators, from a longer list of candidates. The simple tally determines the winners (plurality-at-big voting).
The legislatures of the provinces elect 1 member to the House of Representatives resulting in their prestige of being those who represent "sole districts". Also, the Sangguniang Kabataan (Youth Councils), Sangguniang Barangay (Village Councils), Sangguniang Bayan (Municipal Councils) and some Sangguniang Panlungsod (City Councils) elect the other members. It follows each such truthful or quasi-local government unit does not in the purest sense elect members at-large when analysing their geography equally each fellow member co-exists with the others who have territorial overlap, every bit representing greater or lower-rank districts. The members are in law chosen by the public straight or indirectly. City Council-elected and Sangguniang Panlalawigan (Provincial Board)-elected members are elected such that the city or province may exist dissever into every bit much equally 7 districts, then each elects at to the lowest degree two members.
United states of america [edit]
Commodity I of the United States Constitution provides for direct ballot of members of the House of Representatives. A congressional human action passed in 1967, two U.S.C. § 2c, dictates that representatives must be elected from geographical districts and that these must be single-member districts. Indeed it confirms when the state has a unmarried representative, that will be a representative at-large.
U.S. House of Representatives [edit]
States as at-large congressional districts [edit]
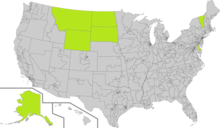
Highlighted in green are the The states congressional districts being states at-large
- Alaska
- Delaware
- Montana (Until 2022 when it will add another commune in the 2022 ballot)
- North Dakota
- South Dakota
- Vermont
- Wyoming
Onetime at-big congressional districts [edit]
Non-voting at-large congressional districts [edit]
- American Samoa
- American Virgin Islands
- District of Columbia
- Guam
- Puerto Rico
- Northern Mariana Islands
Former non-voting at-large congressional districts [edit]
Simultaneous at-large and sub-state-size congressional districts [edit]
This is a table of every such instance. It shows the state of affairs applied to a small, varying grouping of states in iii periods. The 33rd Congress began in 1853; information technology ended two years later on. The 38th began in 1863; the 50th ended in 1889. The 53rd began in 1893; the 89th ended in Jan, 1967, the final such menstruum. This was due to the 1964 instance of Reynolds v. Sims: the Us Supreme Court determined that the general footing of apportionment must be "one person, one vote."[three]
| Congress | Land & Number of at-large seats |
|---|---|
| 33rd | MS (i) |
| 38th | IL (i) |
| 39th | IL (1) |
| 40th | IL (1) |
| 41st | IL (1) |
| 42nd | IL (one) |
| 43rd | AL (two), AR (1), IN (2), LA (1), NY (1), PA (3), SC (1), TN (1), TX (two) |
| 44th | AL (2) |
| 48th | AR (1), CA (two), GA (i), KS (4), NY (1), NC (ane), PA (1), VA (1) |
| 49th | PA (i) |
| 50th | PA (1) |
| 53rd | IL (2), KS (1), PA (two) |
| 54th | KS (i), PA (2) |
| 55th | KS (1), PA (2) |
| 56th | KS (1), PA (2) |
| 57th | KS (1), PA (two) |
| 58th | CO (ane), CT (1), KS (1) |
| 59th | CO (1), CT (1), KS (i) |
| 60th | CO (1), CT (one) |
| 61st | CO (ane), CT (1) |
| 62nd | CO (ane), CT (1) |
| 63rd | AL (ane), CO (2), FL (1), IL (2), MI (ane), MN (1), OH (one), OK (3), PA (four), TX (ii), WA (2), WV (1) |
| 64th | AL (1), IL (2), PA (4), TX (2), WV (1) |
| 65th | IL (two), PA (4), TX (2) |
| 66th | IL (ii), PA (four) |
| 67th | IL (2), PA (4) |
| 68th | IL (2) |
| 69th | IL (two) |
| 70th | IL (two) |
| 71st | IL (2) |
| 72nd | IL (2) |
| 73rd | CT (1), FL (1), IL (2), NY (2), OH (2), OK (one), TX (3) |
| 74th | CT (1), FL (1), IL (two), NY (two), OH (two), OK (1) |
| 75th | CT (1), IL (2), NY (2), OH (2), OK (one) |
| 76th | CT (1), IL (2), NY (ii), OH (ii), OK (1) |
| 77th | CT (ane), IL (2), NY (two), OH (two), OK (1) |
| 78th | CT (1), FL (i), IL (1), NY (ii), OH (1), PA (one) |
| 79th | CT (1), IL (1), OH (1) |
| 80th | CT (1), IL (1), OH (ane) |
| 81st | CT (1), OH (i) |
| 82nd | CT (1), OH (1) |
| 83rd | CT (one), TX (one), WA (ane) |
| 84th | CT (1), TX (ane), WA (1) |
| 85th | CT (1), TX (1), WA (ane) |
| 86th | CT (1) |
| 87th | CT (1) |
| 88th | AL (8), CT (1), Physician (one), MI (i), OH (1), TX (ane) |
| 89th | MD (one), OH (ane), TX (one) |
Country elections [edit]
As of 2021, ten U.Southward. states have at to the lowest degree one legislative sleeping room which uses multi-winner at-large districts:
- Arizona House of Representatives (for all representatives in all sessions)
- New Jersey Full general Assembly (for all representatives in all sessions)
- S Dakota House of Representatives (for all representatives in all sessions)
- Washington House of Representatives (for all representatives in all sessions)
- Maryland House of Delegates (allowed by law even when not used)
- Idaho House of Representatives (allowed by law even when non used)
- Due north Dakota House of Representatives (allowed by constabulary even when not used)
- Vermont Senate and Vermont House of Representatives (immune by police fifty-fifty when not used)
- West Virginia Senate and West Virginia House of Delegates (allowed by law even when not used; will switch to all-single-winner districts for both chambers in 2022)
- New Hampshire House of Representatives (allowed by law even when non used; uses floterial districts which can geographically overlap each other)
In the 1980s, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, South Carolina, and Virginia all moved entirely from multi-winner districts in either chamber, followed by Alaska, Georgia, and Indiana in the 1990s.[iv] Afterward the 2010 United states of america redistricting cycle, Nevada eliminated their 2 remaining multi-member senate districts and implemented unmarried-winner districts in both houses.[v] In 2018, W Virginia passed a law switching all remaining multi-winner Firm of Delegates seats to single-winner districts following the 2020 United States Census.[6]
Local elections [edit]
Since passage of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 and lessening of some historic barriers to voter registration and voting, legal challenges have been made based on at-large election schemes at the county or metropolis level, including in school board elections, in numerous jurisdictions where minorities had been effectively excluded from representation on local councils or boards. An example is Charleston County, South Carolina, which was sued in 2001 and reached a settlement in 2004. Its county commission changed to nine members elected from single-fellow member districts; in 2015 they included six white Republicans and iii African-American Democrats, where the black minority makes up more than than one-third of the population.
In another case, in 2013 Fayette County, Georgia, which had an estimated 70% white majority and twenty% black minority, was ordered past a federal district court to develop single-member districts for election of members to its county quango and its schoolhouse board. Due to at-large voting, African Americans had been unable to elect whatever candidate of their choice to either of these boards for decades.[7] Such local election systems have become subject to litigation, since enabling more representative elections tin can create entry points for minorities and women into the political system, as well as providing more than representative government. In the late 1980s, several major cities in Tennessee reached settlement in court cases to prefer single-member districts in order to enable minorities to elect candidates of their pick to city councils; they had previously been excluded by at-big voting favoring the majority population.[8] Past 2015, voters in two of these cities had elected women mayors who had gotten their start in beingness elected to the urban center quango from single-member districts.
The town of Islip, New York was sued by 4 residents in 2018 for violating the Voting Rights Act by maintaining a discriminatory at-large council organization. I-3rd of Islip's population is Hispanic, but only ane person of colour has ever been elected to a town seat. As part of the settlement reached in 2020, the at-large system will be abolished and replaced by four council districts by 2023.[9]
Some states have laws which further discourage the use of at-big districts. For example, the California Voting Rights Act removes 1 of the criteria required for a successful federal Voting Rights Act claiming, thus resulting in hundreds of cities, school districts, and special districts to move to single member area-based elections.
Some jurisdictions have kept at-large urban center councils and boards. The solution adopted past Cambridge, Massachusetts is to elect council officials via proportional representation for all seats.
Encounter also [edit]
- General ticket
- Plural district
- United states of america Statutes at Big
References [edit]
- ^ Electoral Reform in England and Wales, past Charles Seymour (David & Charles Reprints 1970)
- ^ The Parliaments of England by Henry Stooks Smith (1st edition published in iii volumes 1844-50), 2d edition edited (in 1 volume) by F.Due west.Southward. Craig (Political Reference Publications 1973)
- ^ Reynolds v. Sims, 377 U.S. 533 (1964).
- ^ Lilliard Eastward. Richardson, Jr. and Christopher A. Cooper, "The Mismeasure of MMD: Reassessing the Impact of Multi Fellow member Districts on Descriptive Representation in U.S. State Legislatures," accessed May 27, 2015
- ^ National Conference of Country Legislatures, "Changes in Legislatures Using Multimember Districts after Redistricting," September 11, 2012
- ^ "Bill Status - Complete Beak History".
- ^ ABS Staff, "Fayette Canton at-large election process violates the Voting Rights Human action", Atlanta Blackness Star, 22 May 2013, accessed eleven Apr 2015
- ^ BUCHANAN five. CITY OF JACKSON, 683 F. Supp. 1515 (W.D. Tenn. 1988), Instance Text website
- ^ "Latinos, advocates hail change to how Islip officials are elected". Newsday . Retrieved 2020-x-15 .
Further reading [edit]
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
External links [edit]
- U.South. Business firm of Representatives: Business firm History
- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/At-large
0 Response to "what does it mean to be elected at large"
Post a Comment